Medicare Guidelines, CPT Codes, and Best Practices For RPM
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) has revolutionized healthcare delivery by enabling providers to monitor patients’ health conditions remotely, improving outcomes and reducing costs. However, accurate billing for RPM services requires a thorough understanding of Medicare guidelines, CPT codes, and compliance requirements. This guide covers all aspects of RPM billing to ensure providers can navigate this process effectively.

Patient Eligibility
- Established Patient Requirement: RPM services can only be provided to patients with an existing provider-patient relationship.
- Medical Necessity: Services must be clinically justified and necessary for the patient’s condition.
Data Collection
- Minimum Data Requirement: Practitioners must collect at least 16 days of patient data within a 30-day period for most RPM codes. Treatment management codes (99457, 99458, 98980, 98981) are exempt from this requirement.
Consent and Documentation
- Patient Consent: Explicit consent is required before initiating RPM services, which must be documented in the medical record.
- Thorough Documentation: Providers must record all data collected, monitoring performed, and communication with the patient.
Provider Limitations
- Single Provider Rule: Only one practitioner may bill Medicare for RPM services per patient within a 30-day period.
- Non-Duplication of Services: RPM services must not overlap with other billed services such as chronic care management (CCM).
Key RPM CPT Codes
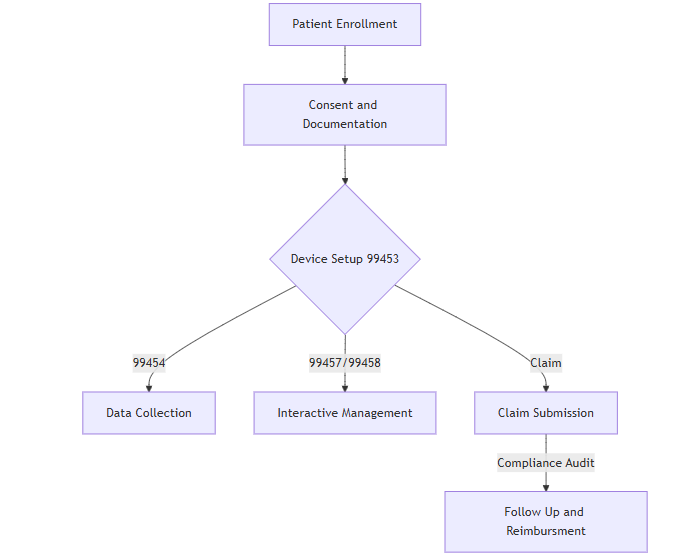
- 99453: Initial setup and patient education on equipment.
- Includes one-time services like installation and setup of monitoring devices.
- 99454: Device supply and data transmission.
- Covers 30 days of device use with programmed alerts.
- 99457: RPM treatment management services.
- Requires interactive communication with the patient or caregiver (first 20 minutes/month).
- 99458: Additional treatment management time.
- Billed for each additional 20 minutes per calendar month.
Understanding Medicare NCCI Edits
The National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) edits aim to prevent improper billing practices. Relevant edits for RPM include:
- Bundling Rules:
- Service Conflicts:
- RPM cannot be billed with CCM services for the same patient on the same day.
Practitioners should review the latest NCCI edits to ensure compliance with billing practices.
Modifier Usage in RPM Billing
Modifiers are essential for accurately reflecting the nature of services provided. Key modifiers include:
- Modifier 25: Indicates a separate, significant E/M service on the same day as a procedure.
- Modifier 59: Identifies distinct procedural services and can bypass certain NCCI edits when appropriately documented.
Reimbursement Rates for RPM Services
Reimbursement rates vary depending on several factors, including geographic location. Providers can use the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule to determine exact reimbursement amounts for each CPT code.
| CPT Code | Description | Average Reimbursement |
|---|---|---|
| 99453 | Initial setup and education | Varies by location |
| 99454 | Device supply and data transmission | Varies by location |
| 99457 | First 20 minutes of management | Varies by location |
| 99458 | Each additional 20 minutes | Varies by location |
Best Practices for RPM Billing
Accurate Documentation
- Record patient consent, monitoring data, and treatment management time.
- Maintain detailed logs of all services provided, ensuring they meet Medicare’s medical necessity criteria.
Regular Updates
- Stay informed about changes in Medicare billing guidelines and NCCI edits to avoid compliance issues.
Cross-Training Staff
- Train billing staff to understand RPM guidelines, modifiers, and compliance rules to reduce claim denials.
RPM Billing Workflow
State-Specific Medicaid Variations
While Medicaid generally follows Medicare’s RPM billing guidelines, states may implement unique requirements. Providers should consult their state’s Medicaid program to verify specific policies and reimbursement rates.
Challenges and Solutions in RPM Billing
Challenges
- Complex Billing Rules: Navigating Medicare and Medicaid guidelines can be overwhelming, especially with frequent updates and complex NCCI edits.
- Documentation Burden: Thorough documentation of consent, data, and services is time-consuming but essential for compliance.
- Claim Denials: Errors in modifiers, overlapping services, or insufficient documentation can lead to rejected claims.
- Technology Integration: Ensuring proper setup and data transmission from RPM devices can present logistical challenges.
Solutions
- Invest in Training: Provide comprehensive training for staff on RPM guidelines, coding, and modifiers to reduce errors.
- Use Billing Software: Leverage technology solutions to streamline the billing process, automate documentation, and check for compliance.
- Partner with Experts: Collaborate with billing and coding specialists to review claims and ensure adherence to Medicare and Medicaid policies.
- Conduct Internal Audits: Regularly audit billing practices to identify and address gaps in compliance or efficiency.
Benefits of Proper RPM Billing
Improved Patient Outcomes
- Continuous monitoring enables early detection of potential health issues, allowing timely interventions and reducing hospital readmissions.
Enhanced Practice Revenue
- Accurate billing ensures maximum reimbursement for RPM services while avoiding penalties for non-compliance.
Better Resource Allocation
- Effective use of RPM reduces the strain on in-person resources, allowing healthcare providers to focus on more critical cases.
Future Trends in RPM Billing
Telehealth Integration
The growing adoption of telehealth complements RPM services, offering a seamless blend of real-time monitoring and virtual consultations. Medicare policies are likely to evolve to integrate these services more effectively.
Expanded Coverage
As more payers recognize the value of RPM, coverage is expected to expand beyond Medicare and Medicaid, including private insurers and employer-sponsored health plans.
Advanced Analytics
AI and machine learning tools will play a significant role in analyzing RPM data, helping providers make data-driven decisions and improving billing accuracy.
Key Takeaways for Providers
- Understand the Guidelines: Familiarize yourself with Medicare and Medicaid requirements, including CPT codes, NCCI edits, and modifiers.
- Document Meticulously: Ensure all aspects of RPM services are well-documented, including patient consent, data collected, and management time.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with changes in RPM billing rules and reimbursement policies.
- Leverage Technology: Use modern software solutions to streamline billing and enhance compliance.
- Collaborate with Experts: Consult with billing and coding professionals to optimize your RPM program and maximize reimbursement.
By implementing these strategies, healthcare providers can not only streamline their RPM billing processes but also contribute to the broader goal of improving patient care through innovative remote monitoring solutions.